Imagine walking through a busy Nigerian market, where brightly coloured food packages compete for your attention. From small shops to large malls, a wide variety of items are attractively displayed. However, hidden beneath these colourful wraps is a danger of too much sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats in majority of these products, which are contributing to Nigeria’s growing health problems.
Without clear, required Front of Pack Warning Labels (FOPWL), consumers are denied the basic right to make informed choices. They unknowingly buy more junk food, which significantly increases the rise of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) which currently contributes to 30 percent Annual deaths in Nigeria.
As a matter of evidence, a recent report titled Junk on Our Plates by Corporate Accountability and Public Participation Africa (CAPPA) underscores this urgent need for FOPWL. The report, based on investigations across seven Nigerian states, reveals how food and beverage companies aggressively market unhealthy foods, often falsely labelling them as “nutritious” or “natural.”
For instance, some sugary yogurts were labelled “not sugary,” while seasoning brands in Northern Nigeria concealed information about their high sodium content but utilised culturally resonant messaging to promote them. It is precisely this kind of lack of openness that strips Nigerians of the ability to make informed food choices, pushing them further into the grip of preventable diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions.
The global rise in NCDs is well-documented, and Nigeria is no exception. A key reason for this is the consumption of heavily processed foods, pushed in the market through aggressive advertising and strategic placement. Without mandatory warning labels to signal danger, consumers are left unaware of the risks. As a result, poor dietary choices become normalised, feeding a cycle of illness that burdens families and the national healthcare system alike.
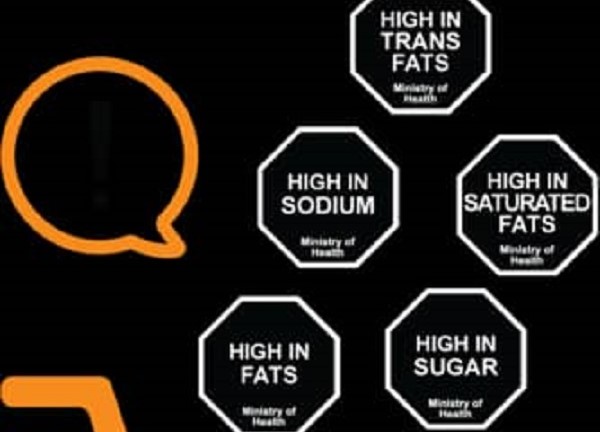
But it is not all doom. International experiences show that countries can successfully reverse these trends with bold regulatory action. In Chile, for example, the introduction of a groundbreaking system of clear, black octagonal warning labels on foods high in critical nutrients of concern, such as sugar, sodium, saturated fats, and trans fats empowered consumers to become more aware, forced companies to reformulate products, and the purchases of sugary drinks to drop by nearly 24 percent within a year.
Mexico and Peru adopted similar systems and recorded significant shifts in consumer behaviour and industry practices. In Peru, marketing claims on processed foods changed drastically as manufacturers reformulated products and utilised warning labels, thereby making their products healthier. Beyond Latin America, other nations are also making progress. In Canada, while not exactly warning labels, nutrition symbols flag high levels of sugar, salt, and saturated fat in food products.
These labels have helped increase consumer awareness and, to some extent, encouraged the development of healthier products. South Africa has published draft regulations for front-of-pack warning labels, backed by research and growing public support. These global examples demonstrate that effective labelling can reduce harmful consumption, reshape industry behaviour, and protect public health.
In addition, the World Health Organisation (WHO) has long endorsed front-of-pack warning labels as one of the most cost-effective tools for preventing diet-related NCDs. In its 2020 guidance, WHO recommended interpretive labelling systems – such as high-visibility warnings and symbols – over complex numeric formats that are difficult for consumers to understand.
According to WHO, such labels not only empower people to make healthier food choices, but also contribute to reducing health inequalities, particularly among lower-income groups who are more vulnerable to aggressive junk food marketing. Countries that have adopted these systems in line with WHO’s guidance have seen measurable declines in the consumption of unhealthy foods, underscoring the effectiveness of labelling as part of a broader nutrition policy framework.
For Nigeria, mandatory warning labels are not just about consumer rights, they are a public health necessity. A clear, standardised system will equip citizens to make better dietary choices, reduce the consumption of junk food, and lessen the burden of NCDs. This proactive approach can stop the rising tide of diet-related diseases and ensure a healthier future for generations to come.
As a matter of urgency, the Nigerian government should enact regulations requiring front-of-pack warning labels for foods high in sugar, sodium, and unhealthy fats. These labels must be visible, understandable, and consistent across all brands. Public education campaigns are also essential to help consumers interpret labels and understand the health risks of poor nutrition. At the same time, manufacturers should be compelled to reformulate products to reduce harmful ingredients and align with public health goals.
Ultimately, embracing transparent Front of Pack Warning labelling policies is a vital step towards building a healthier Nigeria, where informed choices win over the deceptive appeal of junk food and the well-being of the population is prioritized over short-term commercial interests and profits.
By Humphrey Ukeaja, Industry Monitoring Officer at Corporate Accountability and Public Participation Africa (CAPPA)
